I wrote a blog post a few months ago — How to Build an AI Agent for Data Analytics Without Writing SQL. One comment I received was, “This is mostly a toy example; my production jobs are way more complex than this; it won’t be applicable to my job.” — but it misses a bigger point: AI is evolving fast, and it’s reshaping how we build pipelines, write SQL, and even debug. In many companies, AI skills are no longer optional for data engineers. We cannot overlook the fact that AI proficiency is now mandatory.
Let us look at how modern AI, particularly LLMs, RAG, and MCP, is becoming not only relevant, but essential for production-grade data engineering.
Can AI resolve the intricate SQL and data pipeline issues that data engineers face? Please put your skepticism of the potential of AI away, and I can show you its potential and how AI can enhance data engineering.
Let’s examine why there is widespread skepticism about AI’s capacity to handle complex data engineering logic and what has changed.
LLMs: Power and Pitfalls
We equip LLMs with exceptional language comprehension skills. We provide a high-level overview of the necessary code structure and include a sample code, enabling LLMs to handle program writing smoothly. Tools like Cursor and Cline demonstrate how straightforward code generation can be with LLMs.
The developer serves as both a product manager and a QA specialist. For the product manager, you would write the appropriate prompt as a problem statement that clearly describes the AI requirements. For QA, you would understand how to run the code, test the desired outcome, and provide feedback to AI for debugging.
Everything seems simple. However, reality isn’t straightforward.
LLMs are trained by past data; they perform impressively on the data the LLM model has seen but make hallucinations on the data it never saw before.
If the foundation model is not properly post-trained, LLM may make an incorrect guess. ChatGPT may generate confident-sounding code that refers to nonexistent libraries, such as attempting to use a fictional Spark T-digest implementation, which can mislead engineers unfamiliar with the underlying tools.
If LLM can understand a wide range of languages, all we need to do is provide it with the most recent data.
Introducing RAG: Smarter AI with Context
Think of an LLM as a smart but humble student who absorbs any new information that is presented to it. This is the fundamental concept of RAG.
If some library we used is out of date, we give a link to LLM on the updated library documentation to let it learn.
If some facts are out of date, we give the LLM the Wikipedia link to let it learn.
This is the fundamental idea behind RAG — Retrieval-Augmented Generation, a technique that improves the accuracy and relevance of Large Language Models (LLMs) by combining them with external data sources.
RAG is a technique in which a retrieval system searches data from external data sources to identify pertinent information in response to a user’s query. The LLM subsequently employs the retrieved information to produce a more precise and current response.
A good example for a data engineer would be to write an SQL query to retrieve the best-selling product over the last 10 days.
Because LLM does not know the table schema or column names, asking LLM directly may result in an unusable SQL query.
To improve this, we can implement RAG to fetch the schema and columns so LLM can more accurately generate a query.

For RAG, you are basically developing your own customized function to call various tools. If RAG still feels too hacky for you, there are newer options.
The book starts with an overview of AI engineering, explaining how it differs from traditional ML engineering and discussing the new AI stack. The more AI is used, the more opportunities there are for catastrophic failures, and therefore, the more important evaluation becomes. This book discusses different approaches to evaluating open-ended models, including the rapidly growing AI-as-a-judge approach.
AI application developers will discover how to navigate the AI landscape, including models, datasets, evaluation benchmarks, and the seemingly infinite number of use cases and application patterns. You'll learn a framework for developing an AI application, starting with simple techniques and progressing toward more sophisticated methods, and discover how to efficiently deploy these applications.
The Rise of MCP: Standardized Tool Access
While RAG enables LLMs to respond with accurate context, MCP addresses a different issue: how to standardize tool integration.
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is an open standard for connecting AI to databases and tools—like an API layer purposely built for LLMs. Tool providers define a shared interface instead of having every team build one-off integrations with DuckDB, Snowflake, or Spark. LLMs then plug into it seamlessly.
The tool provider who provides the tool will offer the interface to LLM. Now we can subscribe to those tools and have LLMs plug them in for us to use. Since the tool provider created the tools in MCP, they are officially available for use, and everyone adheres to the same standard.

Real-World Example: DuckDB + MCP + LLM
We will use DuckDB from the Cline MCP server in VS Code.

We will use DeepSeek V3 as the LLM model here. To configure DuckDB, you can follow instructions on MCP for DuckDB.
For local testing, all you need to do is make the db path as memory
{
"mcpServers": {
"mcp-server-motherduck": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"mcp-server-motherduck",
"--db-path",
":memory:"
]
}
}
}
We will build another example by loading a dataset from Kaggle — Netflix Movies and TV Shows dataset (CC0: Public Domain)
In Cline, you can test a prompt
load file to DuckDB "~/Downloads/netflix_titles.csv",
then Check the netflix table in DuckDB,
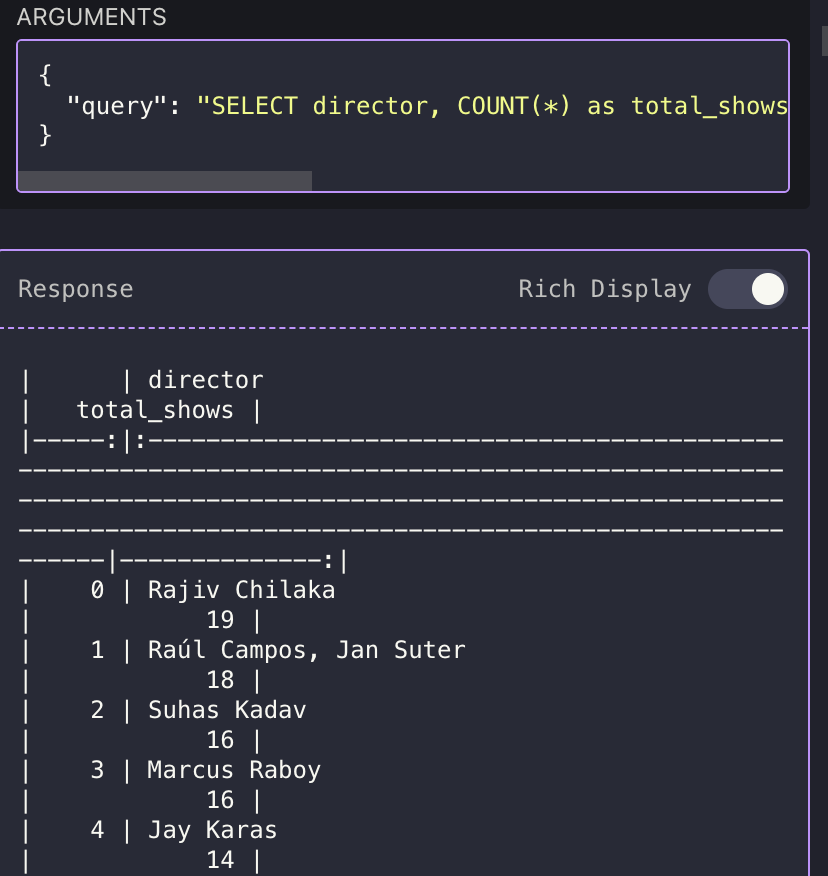
get total number of shows by each director Cline will automatically call DuckDB MCP and load the proper function for our goal, then it will load data into DuckDB and then generate a query to fetch the result.
Let’s try something more complex; we will just use Kaggle notebook for this one, https://www.kaggle.com/code/shivamb/netflix-shows-and-movies-exploratory-analysis, which has done great EPA on top of this dataset.
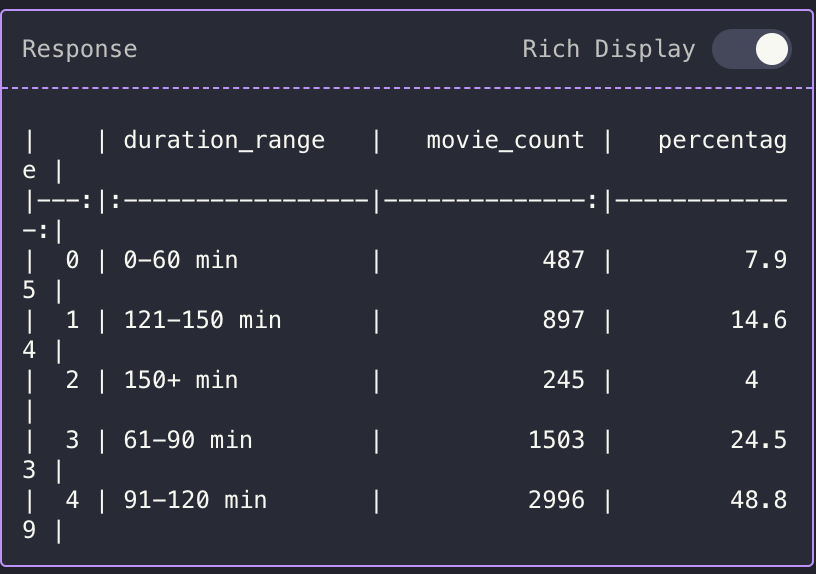
I picked a random query — show me the Distribution of Movie Duration
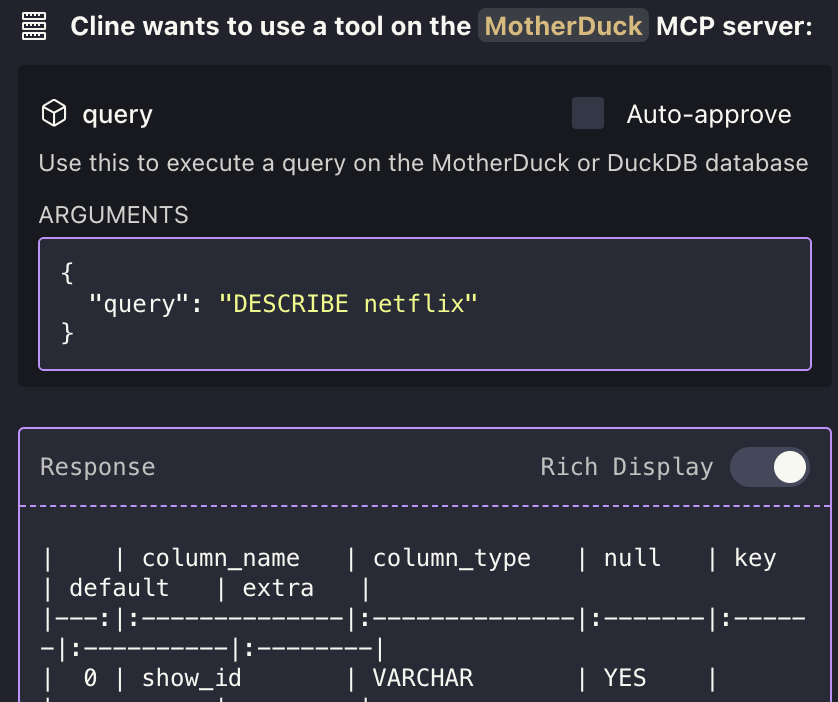
Cline will first check the schema of the DB
It generates the following query. However, the initial attempt failed due to the need for additional data transformations. So it took the error as feedback and tried twice until the issues were resolved.
SELECT
CASE WHEN duration_minutes BETWEEN 0 AND 60 THEN '0-60 min'
WHEN duration_minutes BETWEEN 61 AND 90 THEN '61-90 min'
WHEN duration_minutes BETWEEN 91 AND 120 THEN '91-120 min'
WHEN duration_minutes BETWEEN 121 AND 150 THEN '121-150 min'
ELSE '150+ min' END AS duration_range,
COUNT(*) AS movie_count,
ROUND(COUNT(*) * 100.0 / SUM(COUNT(*)) OVER(), 2) AS percentage
FROM (
SELECT TRY_CAST(TRIM(REPLACE(duration, 'min', '')) AS INTEGER) AS duration_minutes
FROM netflix WHERE type = 'Movie' AND duration IS NOT NULL AND duration LIKE '%min%'
)
WHERE duration_minutes IS NOT NULLGROUP BY duration_rangeORDER BY duration_range
Output
Learn how to empower AI to work for you. This book explains:
- The structure of the interaction chain of your program's AI model and the fine-grained steps in between
- How AI model requests arise from transforming the application problem into a document completion problem in the model training domain
- The influence of LLM and diffusion model architecture—and how to best interact with it
- How these principles apply in practice in the domains of natural language processing, text and image generation, and code
Final Thoughts
We have seen with MCP + LLM that it unlocks the potential for tool integration and simplifies the code development cycle. We have observed that AI can perform data transformation in DuckDB, and I am confident that it can integrate with DBT, Snowflake, and Spark to enhance the workload of data engineers.
AI isn’t optional for day-to-day anymore; it has become a required and essential tool. You can build more tools and productionize your ideas much easier with AI.
AI is becoming a must-have for data engineers, no longer a nice-to-have. Start small. Build an AI-powered tool. You’ll be surprised how much friction you can remove.
About Me
I hope my stories are helpful to you.
For data engineering post, you can also subscribe to my new articles or becomes a referred Medium member that also gets full access to stories on Medium.





